Is an OCR letter in your college or university’s future?
The Office for Civil Rights (OCR) has enforced and settled more than 250 digital accessibility complaints against higher education institutions.
To avoid legal action from the OCR, all web pages and web content on your website meet accessibility guidelines. Your website must be equally accessible to students and parents with disabilities, as well as their non-disabled peers.
But how do you go about implementing such a broad, complex rule?
In this white paper, you’ll gain an understanding of what accessible means and it’s importance to higher education institutions. The most common digital content issues faced by higher education institutions are highlighted along with a roadmap.
Introduction
Higher education institutions are increasingly striving to produce a diverse student body on campus. This includes students with disabilities and their non-disabled peers. Institutions must provide accessible digital content in addition to disabled-friendly student accommodations.
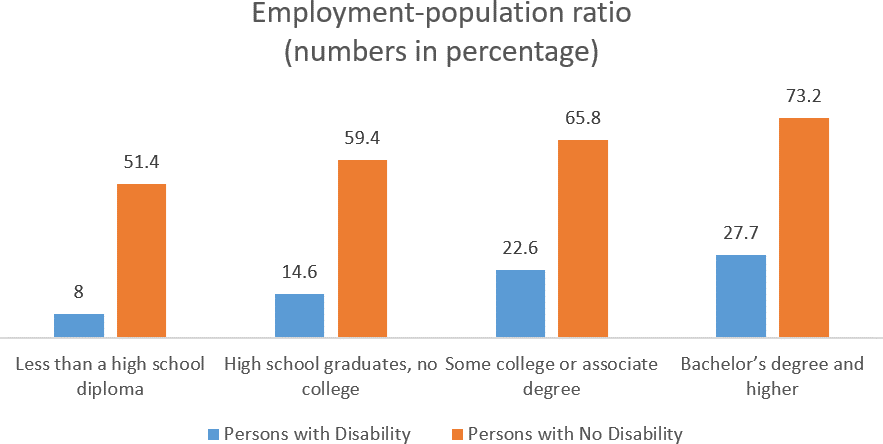
Higher education student disability data in the United States
The U.S. Census Bureau has released the National disability data for undergraduate and post- graduate students with disabilities across the U.S.
- The total student population in the US: 80.5 million
- Students with dyslexia: 8.5 million
- The dyslexic to total student population ratio: 10.6%
Source: U.S. Census Bureau
Understanding Disability Laws
Section 504
The law states that, people with disabilities should not:
- Be denied benefits
- Be excluded from participating in programs
- Face discrimination of any form under any program or activity receiving National federation financial assistance
It offers protection to students who meet all academic and technical standards for admission and participation in education programs. They must also have a disability like:
- A physical or mental impairment that limits one or more major life activities like seeing, hearing, concentrating, reading, and thinking
- Proof of such an impairment
- Being regarded as suffering from such an impairment
The Americans with Disabilities Act
The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) prohibits discrimination against individuals with disabilities in all areas of public life. Title III is clear that ‘Places of Accommodation also includes “Places of Education.’ So it means that schools, courses, and examinations should be accessible to people with disabilities.
Institutions of higher learning have to make all their websites, web pages, and electronic assets including PDFs accessible.
Electronic and information technology accessibility standards
WCAG 2.0
The Web Accessibility Initiative has developed guidelines for web accessibility through the web content accessibility guidelines (WCAG). Higher education institutions can refer to these guidelines for web accessibility.
WCAG 2.0 is the most recent version of these international guidelines. It comprises 12 broad guidelines under these four accessibility principles:
1. Perceivable
The digital product and website information and interface components should be perceivable to students. For example, it should provide text alternatives for non-text content, like images. And students with disabilities should easily hear and see content, including foreground content on the background.
2. Operable
All the user interface components and navigation links should be operable, and functionality should be made possible via the keyboard.
3. Understandable
User interface information and operation should be understandable. For example, all text content should be both readable and understandable. And all web pages should appear and operate predictably.
4. Robust
The site and digital content should be robust enough to be reliably interpreted by multiple user agents, including assistive technologies. There should be maximum compatibility with current and future user agents, including assistive technologies.
Rise in ADA lawsuits against colleges and universities
There is an increase in the number of ADA lawsuits filed against colleges and universities. This is due to inaccessible websites, online courses, textbooks, or classroom materials. There is also an increase in the number of complaints filed with the OCR about inaccessible digital documents and technologies.
In 2000, the federal education department closed 550 website accessibility investigations against higher education institutions. Many higher education institutions like MIT and Harvard University have settled the lawsuits filed against them recently. They committed to developing digital documents in PDF formats accessible to everyone.
Higher education accessibility enforcement actions
The Justice Department settles with Louisiana Tech University over inaccessible course materials
The Justice Department has reached a settlement with Louisiana Tech University to remedy violations of the ADA. The settlement resolves allegations that the University used an online learning product that was inaccessible to a blind student. The student’s lack of access to the course materials persisted nearly one month into the University quarter. The student was compelled to withdraw from the course since he fell behind in learning compared to his peers.
Justice Department Moves to Intervene in Disability Discrimination Lawsuit Alleging that Miami University Uses Inaccessible Educational Technologies and Course Materials
The Justice Department has intervened in a private lawsuit alleging disability discrimination by Miami University in Oxford, Ohio. The lawsuit alleges that Miami University has violated Title II of the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). Current and former students with disabilities were forced to use inaccessible course materials and LMS.
Settlement Between Penn State University and National Federation of the Blind
The university has reached an agreement with the National Federation of the Blind. It will carry out an accessibility audit and develop and an EIT Accessibility Policy Statement. The University will also conduct training and provide support for staff and faculty. Penn State has also agreed to make its website and content accessible.
Digital Accessibility in Higher Education
Digital accessibility refers to accessible electronic and information material that is available to all, including those with disabilities. In higher education, learning material is available to students with disabilities as well as non-disabled students.
Generally, students depend on specially designed technology to complete computer and mobile device tasks. These devices are assistive technology that provides students with disabilities equal employment, education, and opportunity in life.
Today, educators, colleges, and universities have a legal responsibility to provide accessible platforms and instructional materials to all their students. Besides, accessible materials like PDF files, Word, Excel documents ensure all students can participate and benefit through equal learning opportunities.
Why is digital accessibility so important in higher education?
Accessibility means making it possible for all students, regardless of physical or developmental impairment, to access course materials. A course is accessible when every student can perceive, and navigate course content, submit assignments, and use all course tools.
Accessibility of online courses is important because?
A significant number of students have disabilities that can make it difficult for them to take an online course. According to the National Center for Education Statistics, 17% full-time undergraduate and 12% postgraduate students report having a disability. 21% part-time undergraduate students and 12% postgraduate students reported a disability. Many students with disabilities prefer online courses to face-to-face courses.
Digital accessibility in higher education benefit many students, not just those with documented disabilities. Just as physical accessibility measures are useful, accessible online courses help a wide range of students.
Most problematic digital content issues faced by higher education institutions and possible solutions
Higher education institutions struggle to make their digital content accessible mainly due to lack of content creators and trained faculty. The most problematic digital content issues are:
- Inappropriate headings
- Inaccessible documents
- Useless alt text
Digital Accessibility Roadmap
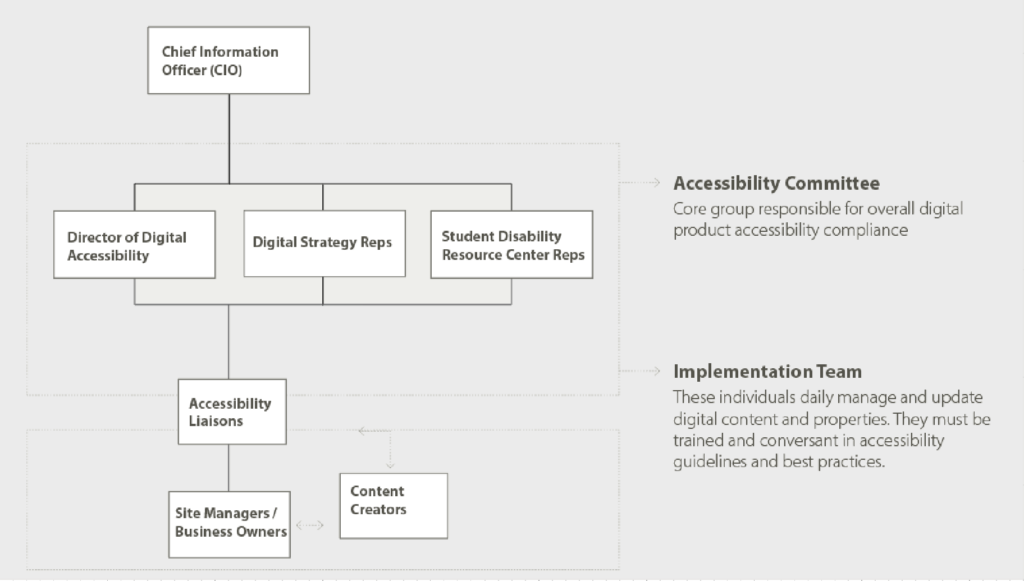
Higher education institutions must have a clear roadmap in place to implement digital accessibility on their campus. The roadmap includes various stakeholders and resources who perform specific roles and report to their superior in a time-bound manner.
Roles and responsibilities
Chief Information Officer
The CIO is responsible for digital accessibility compliance.
Director of Digital Accessibility
The Director is responsible for all accessibility efforts and serves as a point of contact for the Accessibility Committee.
Digital Accessibility Committee
The Committee discusses high-level strategies to ensure the institution is on track for digital accessibility compliance.
Digital Strategy Representatives
The campus Representatives participate in the Accessibility Committee and oversee new major digital initiatives.
Student Disability Resource Center Representatives
They serve on the Committee and guide accessibility related to educational efforts.
Institutions can adopt a few practical steps to ensure their digital content, online delivery systems, and technologies are fully accessible. These steps include:
- Check all electronic and information technology like digital content, websites, LMS, classroom technology, library databases, etc., for accessibility standards.
- Involve students, staff, and faculty in the usability testing process and develop a plan to remediate accessibility issues.
- Prioritize optimal accessibility standards right from the start and include it in the acquisition and procurement process.
- Make it mandatory that all vendors provide an accurate product Voluntary product accessibility template.
- Train the staff, faculty, and students about accessibility issues and standards.
- Lastly, accessibility isn’t a project. It’s a long-term commitment to bring your campus into accessibility compliance in all aspects of campus life.
Every institution must have a long-term digital accessibility plan to meet ADA standards and WCAG guidelines.
- Form a collaborative planning team with various contributors and stakeholders.
- Assess needs and challenges.
- Integrate accessibility into your school’s procurement process.
- Determine who owns what.
- Perform an accessibility audit.
- Develop goals and objectives to put an actionable accessibility plan in place.
- Introduce cross-campus training.
- Conduct ongoing evaluations.
Digital Access and Inclusion for Higher Education Institutions
codemantra enables higher education institutions to provide accessible learning content to students with disabilities. Our AI-driven platform automates digital document accessibility compliance. It captures, classifies, and extracts data from documents. The output is transformed to any desired format.
- Audit, assess, and make digital information accessible in any format – PDF, Excel, Word, PowerPoint, and ePub.
- 100% compliance with Federal and State Laws – ADA, Section 508, WCAG 2.1 Level AA
- Eliminate disproportionate burden using our scalable, AI-driven modules
- Create accessible course materials – Make all course material accessible and compliant as per accessibility guidelines
Conclusion
The number of students with disabilities enrolling in colleges is set to increase in the coming years. TO avoid entangling in lawsuits and having to pay hefty fines, institutions must lay out a detailed accessibility plan.
Inclusive instructional materials and information communication technology as part of digital accessibility initiatives are a must for every institution.








